Ceramic capacitors are widely used passive electronic components that store and release electrical energy. Known for their excellent electrical characteristics, compact size, and high performance in various applications, these capacitors are an essential part of modern electronic devices. Below are the main features and applications of ceramic capacitors, adapted to the standards and terminology relevant to the United States and the United Kingdom.
Structure and Operation
- Dielectric Material: Ceramic capacitors use ceramic as the dielectric material, providing a high dielectric constant, which contributes to their compact size and effectiveness.
- Shape: Available in various shapes, including SMD (Surface-Mount Device) and radial, which allows for easy integration onto printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Key Characteristics
- Capacitance: Ceramic capacitors are available in a wide range of capacitances, from a few picofarads (pF) up to hundreds of microfarads (µF).
- Tolerance: The tolerance generally ranges from ±1% to ±10%, providing high precision for many applications.
- Rated Voltage: These capacitors can operate at different voltages, typically from 10V to 500V, with options available for even higher voltages.
- Operating Temperature: The operational temperature range is typically from -55°C to +125°C, with some variants capable of withstanding even more extreme temperatures.
- Stability: Ceramic capacitors exhibit excellent thermal stability and resistance to humidity variations, maintaining their electrical properties over time.
Typical Applications
- Decoupling: Used for decoupling circuits, helping to stabilize voltage and reduce unwanted noise.
- Signal Filtering: Employed in high-frequency filters due to their low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and low dielectric losses.
- Oscillators: Utilized in oscillator circuits because of their ability to maintain a stable capacitance value.
- High-Frequency Circuits: Ideal for high-frequency applications where low ESR and excellent high-frequency performance are crucial.
Advantages
- High Capacitance in Small Volume: These capacitors offer high capacitance in a compact size, making them ideal for modern, space-constrained devices.
- Low Inductance: Especially useful in high-frequency applications due to their low inductance, ensuring better performance.
- Cost: Ceramic capacitors are typically economical and widely available, making them a popular choice for various applications.
Disadvantages
- Capacitance Variation with Temperature: Some classes of ceramic capacitors, especially Class II and III, may experience significant capacitance variation with temperature changes.
- Microphonics: In certain applications, ceramic capacitors may exhibit microphonics, where mechanical vibrations translate into electrical variations, leading to potential performance issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between Class I, II, and III ceramic capacitors?
- Class I capacitors have the most stable temperature and voltage characteristics but lower capacitance. They are ideal for precision applications.
- Class II and III capacitors provide higher capacitance but exhibit more significant capacitance variation with temperature. They are often used where cost and size are more important than precision.
2. Can ceramic capacitors be used in high-frequency circuits?
Yes, ceramic capacitors are ideal for high-frequency applications due to their low ESR and inductance, which make them effective at filtering high-frequency signals.
3. Why do ceramic capacitors sometimes experience microphonics?
Microphonics can occur in ceramic capacitors because mechanical vibrations can induce electrical noise. This can be an issue in sensitive audio or high-precision circuits.
4. What is the typical lifespan of a ceramic capacitor?
Ceramic capacitors typically have a long lifespan when used within their specified voltage and temperature ranges. However, their performance may degrade if exposed to extreme conditions for prolonged periods.
If you liked this article, consider sharing it on social media, this will help to spread knowledge, leave your comment below so we can know your opinion.
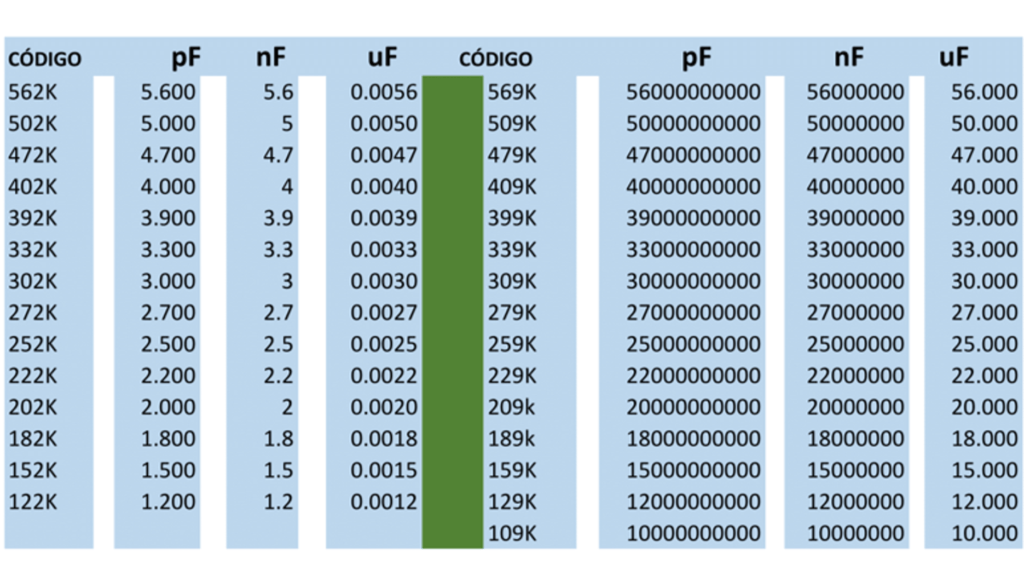
| Description of Values in Picofarads (pF) / Nanofarads (nF) | Equivalent Codes |
|---|---|
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1,2pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1,5pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor1,8pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 2,2pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 2,7pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 3pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 3,3pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 3,9pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 4,7pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 5,6pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 6,8pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 7pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 10pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 12pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 13pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 15pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 18pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 22pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 27pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 33pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 39pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 47pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 56pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 68pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 82pF x 50V | - |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 100pF x 50V | 101 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 120pF x 50V | 121 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 150pF x 50V | 151 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 180pF x 50V | 181 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 220pF x 50V | 221 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 270pF x 50V | 271 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 330pF x 50V | 331 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 390pF x 50V | 391 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 470pF x 50V | 471 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 560pF x 50V | 561 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 680pF x 50V | 681 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 820pF x 50V | 821 |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1nF x 50V | (0,001uF/1KpF/102) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1,2nF x 50V | (1K2/1,2KpF/122/1n2K) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1,5nF x 50V | (1K5/1,5KpF/152) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 1,8nF x 50V | (1K8/1,8KpF/182) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 2,2nF x 50V | (2K2/2,2KpF/222) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 2,7nF x 50V | (2K7/2,7KpF/272) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 3,3nF x 50V | (3K3/3,3KpF/332) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 3,9nF x 50V | (3K9/3,9KpF/392) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 4,7nF x 50V | (4K7/4,7KpF/472) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 5,6nF x 50V | (5K6/5,6KpF/562) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 6,2nF x 50V | (6K2/6,2KpF/622) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 6,8nF x 50V | (6K8/6,8KpF/682) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 7,2nF x 50V | (7K2/7,2KpF/722) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 10nF x 50V | (0,01uF/10K/10KpF/103) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 15nF x 50V | (0,015uF/15K/15KpF/153) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 22nF x 50V | (0,022uF/22K/22KpF/223) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 27nF x 50V | (0,027uF/27K/27KpF/273) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 33nF x 50V | (0,033uF/33K/33KpF/333) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 39nF x 50V | (0,039uF/39K/39KpF/393) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 47nF x 50V | (0,047uF/47K/47KpF/473) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 56nF x 50V | (0,056uF/56K/56KpF/563) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 68nF x 50V | (0,068uF/68KpF/683) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 82nF x 50V | (0,082uF/82K/82KpF/823) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 100nF x 50V | (0,1uF/100K/100Kpf/104) |
| Ceramic Disc Capacitor 220nF x 25V | (0,22uF/220K/220KpF/224) |