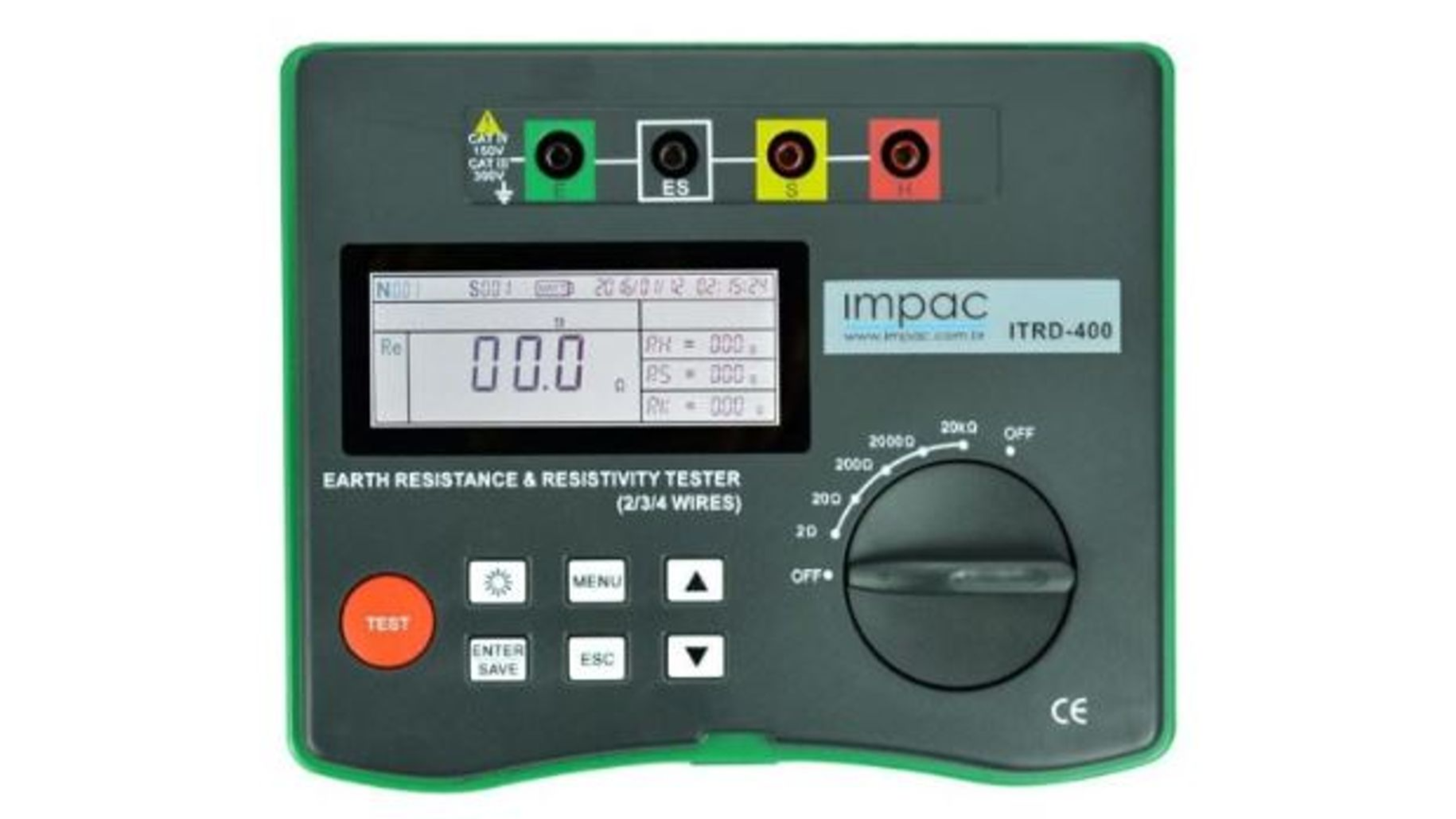
An Earth Resistance Tester is a crucial instrument used by engineers and technicians to measure soil resistance to electrical discharges. This measurement evaluates the efficiency of grounding systems, ensuring they function properly and provide safety for equipment and people.
How Does an Earth Resistance Tester Work?
Grounding is essential in electrical installations to prevent power surges or overloads from damaging equipment. When analyzing a grounding system, the impedance values of electrodes are assessed according to electrical codes and engineering standards.
The Earth Resistance Tester measures this impedance: the lower the impedance, the better the grounding performance. Ideally, grounding resistance should be below 10 Ohms, while values above 30 Ohms may pose risks.
Types of Earth Resistance Testers
Different applications and precision requirements dictate the type of tester to use. The main types include:
1. Three-Wire Earth Resistance Tester
This traditional tester measures soil resistance by evaluating the voltage along the path of the electric current back to the grounding electrode. It is ideal for open systems and industrial environments.
- Features: Measures ground resistance with high accuracy using three electrodes.
- Applications: Suitable for isolated grounding systems.
2. Clamp-On Earth Resistance Tester
This type measures resistance in closed circuits without disconnecting the ground system, making it practical and efficient for quick maintenance.
- Features: Measures resistance through induction without auxiliary electrodes.
- Applications: Ideal for substations and electrical panels.
3. Digital Earth Resistance Tester
Advanced models offering precise measurements with features like data storage and graphical analysis.
- Features: High precision, digital display, and advanced options.
- Applications: Used in complex industrial systems.
4. Portable Earth Resistance Tester
Compact and lightweight, this tester is ideal for fieldwork requiring mobility.
- Features: Easy to transport without compromising accuracy.
- Applications: Residential and small-scale commercial projects.
5. High-Frequency Earth Resistance Tester
Used for measuring resistance at higher frequencies, suitable for specific installations such as communication systems.
- Features: Operates at higher frequencies.
- Applications: Lightning protection systems (SPDA).
Steps for Measuring Ground Resistance
- Position the Electrodes:
- Fixed Electrode: Acts as a reference point (ground rod).
- Current Electrode: Positioned at least three times the length of the fixed rod.
- Voltage Electrode: Placed 62% of the distance between the fixed and current electrodes.
- Take Measurements:
- Connect the tester to the electrodes.
- Measure and compare the resistance values with established standards.
- Improve Ground Resistance:
- If resistance is too high, increase the grounding mesh by adding interconnected rods.
Precautions When Using an Earth Resistance Tester
- Ensure batteries are correctly installed.
- Use the appropriate testing function.
- Avoid active electrical circuits.
- Protect the tester from prolonged sun exposure.
- Remove batteries when not in use.
- Wear safety equipment such as insulated gloves and shoes.
Summary of Earth Resistance Testers
Type | Main Application | Notable Advantage |
|---|---|---|
Three-Wire Tester | Isolated systems | High accuracy in complex systems |
Clamp-On Tester | Maintenance and inspections | Measures without disconnection |
Digital Tester | Complex industrial installations | Advanced features |
Portable Tester | Field measurements | Compact and transportable |
High-Frequency Tester | SPDA and communication systems | Operates at high frequencies |
Conclusion
The Earth Resistance Tester is indispensable for ensuring electrical safety in residential, industrial, and commercial installations. Proper use and maintenance prevent equipment damage and enhance safety for people.
FAQ
- What is an Earth Resistance Tester?
- It is an instrument used to measure soil resistance and evaluate the efficiency of grounding systems.
- Why is grounding important?
- Grounding directs leakage currents to the ground, preventing damage and ensuring safety.
- How does the tester measure soil resistance?
- It assesses soil’s ability to dissipate electrical currents using sensors.
- What is the ideal grounding resistance?
- Generally, values below 10 Ohms are safe, depending on technical standards.
- Who should use an Earth Resistance Tester?
- Qualified professionals, such as electrical engineers, should use it for accurate and safe measurements.